Big Bang and Amateurs
Some people are interested about the universe knowledge and his developement. The main theory, named the BigBang, describes an universe explosed, about 15 billions of years ago, from a very warm and compact point, and which is expanding itself with a speed of 25 km/sec per million of year-ligth-distance (* M.y.l.) .
The most convincent proof of the BigBang is the atomic lines movement observation (Doppler effect, redshift): all that we observe in the deep space, is going away much faster than farer it seems and so the redshift means also distance and age.
Atomic lines are moving for many reasons, but mostly because of the movement of the lightsource, of the observer or of the transmitting bed...
But, also in the sky, many things are "strange":
- the celestial objects with high redshift (quasar, qso) are often blue and punctiform
- the quasars doesn't shows a good relation between the redshift (distace, age) and apparent magnitude
- the qso have not an uniform distribution in the sky
- in the study of quasars we must admit superluminar speeds
- the interposition of a galaxy produce effects on the mesurement of the redshift
- the problem of the missing mass is still without solution
- some qso seems to be associated phisically with near galaxies and this association is proportional to their distance
- the associated galaxies have different redshift
- the dominant galaxies have very low redshift
- someone detects the quantization of the redshift in associated qso and clusters of galaxies
- the mistery of acceleration of the Pioneer 10 and 11 is still a mystery
An amateur then, could propose an aproximative formula for explain these 11 "strange" points:
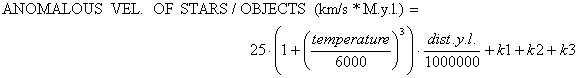
where k1 are plasma-clouds, k2 are gradients of plasma and k3 are the proper motus of the object. These k could be neglected if the distance vale is very high or the data statistics are homogeneous. The anomalies (REDSHIFT, VEL RAD ANOM, ACCEL ANOM, SISTEMATIC SHIFT,.) are proportional to the distance and to the cubed temperature in a fractionary complex.
And so the expansion simply doesn't exists, almost all is without movement and we must extimate the distances in different ways.
Perhaps Einstein was saying: "A good theory must explain the known phenomenas and forecast new controllable phenomenas"
An other amateur could also make consequent previsions and someone else could prove if they are false:
- the warmer a stars is, the higher his rad.vel. is. (rad.vel is proportional to the star temperature)
- the farer stars have higher radial velocity
- the stars placed near to the warm stars have normal r.v.
- in the warmer stars, the proper motus speeds are normal
- the double stars have same anomalies in the r.v.
- same r.v. abnormality detected in open clusters with warm stars
- same anomal v.r. in the galaxies for the warm stars
- inside the galaxy clusters, anomal redshift for the active galaxies
- explication of other anomalies in the Pioneers acceleration
- in the farer clusters of galaxies ,bigger differences in the redshift's components
- interaction of coherent light with plasma in movement (RAMAN effect, chained wave and the theory of autostructured light).
A further amateur could also perform two questions:
